The human heart
The human heart
Patent foramen ovale - PFO
What is it?
In patent foramen ovaleThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely… (PFOThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely…), the tissue of the cardiac septumThe septum (from the Latin "saeptum" - border, fence) is a wall. The cardiac septum separates the left and right part of the heart. overlaps to form a tunnel-like connection between the right and left atria. With a PFOThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely… the connection between the atria is not permanent but opens only sometimes. If this happens, blood can flow from the right to the left atrium.
How does the defect occur?
In unborn children the cardiac septum is not closed completely. The so-called foramen ovale creates a connection between the two atria, thus enabling the blood to flow from the right into the left atrium. As the unborn child does not need a functional pulmonary circulation yet, the latter is bypassed by the connection between the two atria. Following birth, this connection starts to close. If this does not happen, it is called a patent foramen ovale.
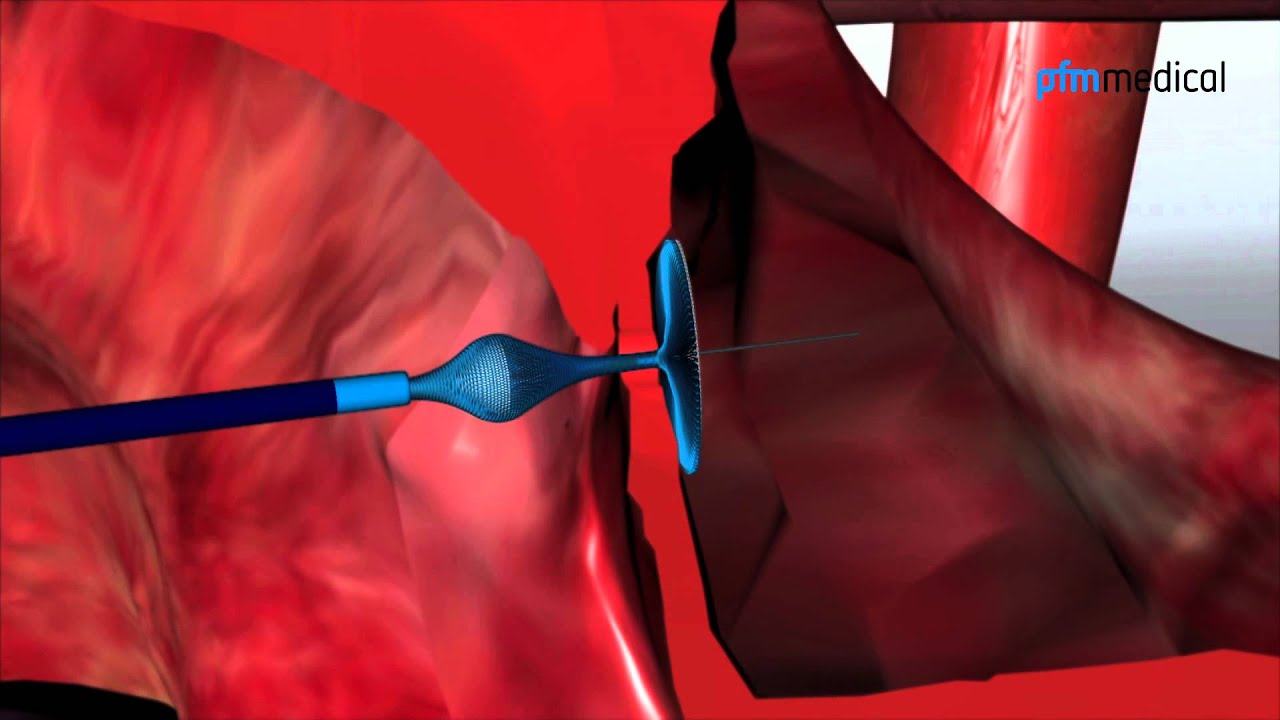
How is the PFO treated?
Often the PFOThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely… is so small that it does not represent a serious problem and does not need to be corrected. The interchange of small amounts of blood between the two atria per se is not critical. However, if the PFOThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely… is larger, or if an adult patient has a tendency toward clot formation, interventional closure can make sense.
As a rule, transoesophageal echocardiography is first performed to determine the size of the PFOThe foramen ovale is an oval opening in the wall separating the left and right upper chambers of the heart. In the unborn child the cardiac septum is not closed completely…. A catheter is then inserted into a blood vessel in the inguinal area and advanced into the heart. Through this cahtheter, an occluder of the right size is advanced into the heart and placed in the defect. The catheter is removed, the occluder closes the hole and becomes firmly ingrown over time.
Here you can see how the Nit-Occlud® PFO occluder is put into place.